Chapter 4- Measuring the Success of Strategic Initiatives
Measuring Information Technology's Success
- Key performance indicator - measures that are tied to business drivers
- Metrics are detailed measures that feed KPIs
- Performance metrics fall into the nebulous area of business intelligence that is neither technology,nor business centered, but requires input from both IT and business professionals.
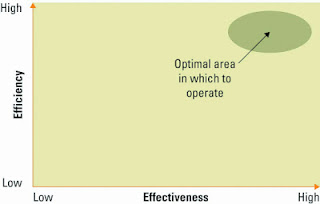
- Efficiency IT metrics -measures the perfomance of the IT system itself including throughput ,speed ,and availability.
- Effectivesness IT metrics - measures the impact IT has business processes and activities including customer satisfation ,conversion rates, and sell-through increase.
- Regardless of what is measured , how it is measured, and whether it is for the sake of efficiency or effectiveness, there must be BENCHMARKS- baseline values the system seeks to attain
- Benchmarking- a process of continuosly measuring system result, comparing those result to optimal system performance (benchmark values),an identifying steps and procedures to improves system perfomance.
The interrelationships of efficiency and effectiveness IT Metrics
-Efficiency IT metrics focus on technology and include:
- Throughput - the amount of information that can travel through a system at any point
- Transaction speed - the amount of time a system takes to perform a transtraction.
- System availability - the number of hours a system is available for user.
- Information accuracy - the extent to which a system generates the correct results when executing the same transaction numerous times.
- Web traffic - includes a host of benchmarks such as the number of page views, the number of unique visitors, and the average time spent viewing a Web page.
- Response time - the time it takes to respond to user interactions such as a mouse click.
- Usability - The ease with which people perform transactions and/or find information. A popular usabilty metric on the internet is degrees of freedom, which measures the number of clicks required to find desired information.
- Customer satisfaction - Measured by such benchmarks as satisfaction surveys, percentage of existing customers retained, and revenue dollars per customer.
- Conversion rate - the number of customers an organization "touches" for the first time and persuades to purchase its products or services. this is a popular metric for evaluating the effectiveness of banner, pop-up, and pop-up under ads on internet.
- Financial - Such as return on invesment ( the earning power of an organization's assets), cost-benefit analysis(the comparison of projected revenues and cost including development, maintenance, fixed, and variable), and break-even analysis (the point at which constant revenues equal ongoing costs)
-It is inefficient for an organization to implement Internet security, since it slows down processing
- However, to be effective it must implement internet security
- secure internet connection must offer encryption and Secure Sockets Layers (SSL denoted by the lock symbol in the lower right corner of a browser)
Metrics for strategic Initiatives
- Metrics for measuring and managing strategic intiatives include:
- Supply chain mangement(SCM) metrics
-Customer relationship management (CRM) metrics
-Business process reengineering (BPR) metrics
-Enterprise resource planning(ERP) metrics
1.WEB SITE METRICS
- Abandoned registrations: Number of visitors who start the process of completing aregistration page and hen abandon the activity.
- Abandoned shopping carts: Number of visitors who create a shopping cart and start shopping and the abandon the activity before paying for the merchandise.
- Click through: Count of the number of people who visit a site, click on an ad, and are taken to the site of the advertiser.
- Conversion rate: Percentage of pontential customers who visit a site and actually buy something.
- Cost-per-thousand(CPM):Sales dollars generated per dollar of advertising. This is commonly used to make the case for spending money to appear on a search engine.
- Page exposure: Average number of page exposures to an individual visitor .
- Unique visitors: Number of unique visitors to a site in a given time. this is commonly used by Nielsen/ Net ratings to rank the most popular Web sites.
- Back order: An unfilled customer order. Aback order is demand(immediate or past due )against an item whose current stock level is insufficient to satisfy demand.
- Customer order promised cycle time:The anticipated or agreed upon cycle time of a purchase order. It is gap between the purchase order creation date and the requested deluvery date.(Dominos delivery order)
- Customer order actual cycle time: The average time it takes to actually fill a customer's purchase order. This measure can be viewed on an order line level.
- Inventory replenishment cycle time: Measure of the manufacturing cycle time plus the time included to deploy the product to the appropriate distribution center.
- Inventory turn over: the number of times that a compay's inventory cycles or turns over per years.it is one of the most commonly used supply chain metrics.
- customer relationship management metrics measure user satisfaction and interaction and include:
-Service metrics
-Marketing metrics






Comments
Post a Comment